深度学习是在b站跟着李沐老师学的,选的kaggle竞赛也是动手学深度学习里的.
因为大二要跟老师做大创,所以做些kaggle竞赛来检验一下学习成果. 同时也是记录一下图像分类的方法方便以后再使用,代码是NEKO KIKU的simple resnet baseline. 自己完全理解后写的本文.
关于数据
| 训练样本数 | 预测样本数 | 类别数 | 图片尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18353 | 8800 | 176 | 224*224 |



创建自己的Dataset
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, csv_path, file_path, mode='train', valid_ratio=0.2,
resize_height=224, resize_width=224):
# csv_path (string): csv 文件路径
# img_path (string): 图像文件所在路径
# mode (string): 训练模式还是测试模式
# valid_ratio (float): 验证集比例
# resize_height, resize_width (int): 调整图片尺寸
self.resize_height = resize_height
self.resize_width = resize_width
self.file_path = file_path
self.mode = mode
self.data_info = pd.read_csv(csv.path, header=None)
# header=None为去掉表头部分
self.data_len = len(self.data_info.index) - 1
self.train_len = int(self.data_len * (1 - valid_ratio))
#训练样本数
if mode == 'train':
self.train_image = np.asarray(self.data_info.iloc[1:self.train_len, 0])
self.train_label = np.asarray(self.data_info.iloc[1:self.train_len, 1])
self.image_arr = self.train_image
self.label_arr = self.train_label
elif mode == 'valid':
self.test_image = np.asarray(self.data_info.iloc[self.train_len:, 0])
self.test_label = np.asarray(self.data_info.iloc[self.train_len:, 1])
self.image_arr = self.train_image
self.label_arr = self.train_label
elif mode == 'test':
self.test_image = np.asarray(self.data_info.iloc[1:, 0])
self.image_arr = self.test_image
self.len = len(self.image_arr)
print('{}数据集,{}个样本'.format(mode, self.len))
def __getitem__(self, index):
# 获取文件名
image_name = self.image_arr[index]
# 读取图片
img = Image.open(self.file_path + image_name)
# 训练模式进行图像增广
if self.mode == 'train':
transform = transforms.Compose([
# 图像裁剪
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(64, scale=(0.08, 1.0), ratio=(3.0 / 4.0, 4.0 / 3.0)),
# 随机水平翻转
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
# 修改亮度,对比度,饱和度
transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.4, contrast=0.4, saturation=0.4),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
else:
# 验证集与测试集无需图像增广
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
# 图像增广
img = transform(img)
if self.mode == 'test':
# 测试集仅返回图片
return img
else:
# 训练集返回图片与对应的类别标签
num_labels = class_to_num[self.label_arr[index]]
# 此处需先进行类别到数字的映射
return img, num_labels
def __len__(self):
return self.len
继承pytorch的dataset,创建自己的dataset.
可以将数据转换为可迭代的iter,便于训练和预测.
主要实现为在__init__中读取csv文件,提取特征与标签.
在__getitem__中返回特征与标签(测试集仅返回特征)并进行图像增广.
在__len__中返回样本数.
resnest50模型使用
ResNeSt50残差网络
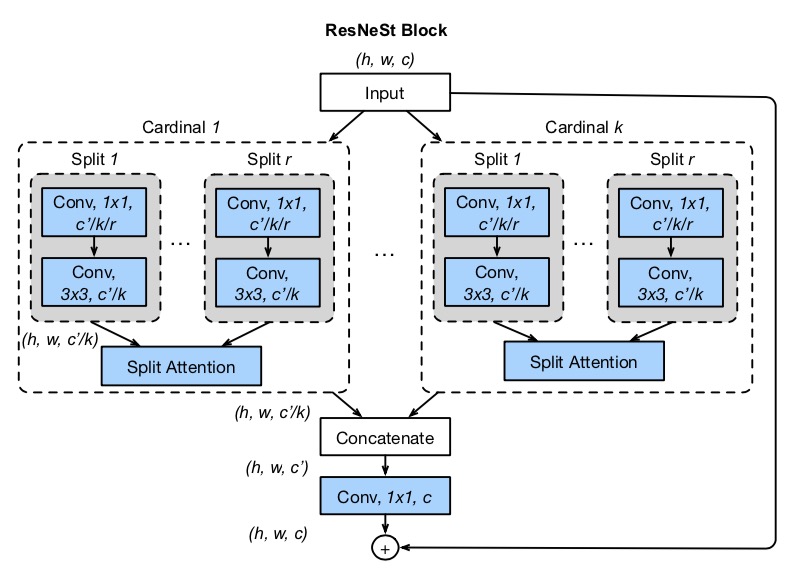 ResNeSt 的全称是:Split-Attention Networks,特别引入了Split-Attention模块。
ResNeSt 的全称是:Split-Attention Networks,特别引入了Split-Attention模块。
具体还不懂,爬去看论文了:(
resnest库安装
pip install resnest --pre
resnest50导入
from resnest.torch import resnest50
模型使用
def set_parameter_requires_grad(model, feature_extracting):
if feature_extracting:
model = model
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def res_model(num_classes, feature_extract=False, use_pretrained=True):
# pretrained=True导入模型预训练参数
model_ft = resnest50(pretrained=use_pretrained)
# set_parameter_requires_grad函数冻住前面的层
set_parameter_requires_grad(model_ft, feature_extract)
# 修改全连接层
num_ftrs = model_ft.fc.in_features
model_ft.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_ftrs, num_classes))
return model_ft
# 176为当前数据集类别数
model = res_model(176)
训练/测试/预测
超参数设置
| 学习率 | 权重衰减 | 训练轮数 | 损失函数 | 优化器 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1e-4 | 1e-3 | 50 | 交叉熵损失 | Adam |
训练与测试
learning_rate = 1e-4
weight_decay = 1e-3
num_epoch = 50
model_path = '/kaggle/working/pre_res_model.ckpt'
model = res_model(176)
model = model.to(device)
model.device = device
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)
n_epochs = num_epoch
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
model.train()
train_loss = []
train_accs = []
for batch in tqdm(train_loader):
imgs, labels = batch
imgs = imgs.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
logits = model(imgs)
loss = criterion(logits, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
acc = (logits.argmax(dim=-1) == labels).float().mean()
train_loss.append(loss.item())
train_accs.append(acc)
train_loss = sum(train_loss) / len(train_loss)
train_acc = sum(train_accs) / len(train_accs)
print(f"[ Train | {epoch + 1:03d}/{n_epochs:03d} ] loss = {train_loss:.5f}, acc = {train_acc:.5f}")
model.eval()
valid_loss = []
valid_accs = []
# tqdm为进度条显示
for batch in tqdm(val_loader):
imgs, labels = batch
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(imgs.to(device))
loss = criterion(logits, labels.to(device))
acc = (logits.argmax(dim=-1) == labels.to(device)).float().mean()
valid_loss.append(loss.item())
valid_accs.append(acc)
valid_loss = sum(valid_loss) / len(valid_loss)
valid_acc = sum(valid_accs) / len(valid_accs)
print(f"[ Valid | {epoch + 1:03d}/{n_epochs:03d} ] loss = {valid_loss:.5f}, acc = {valid_acc:.5f}")
# 更新最佳模型并保存
if valid_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = valid_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
print('saving model with acc {:.3f}'.format(best_acc))
tqdm显示训练进度条很好用:D
每轮训练时储存最好的模型参数,发现损失不下降了可以提前终止训练,直接进行预测.
预测
saveFileName = '/kaggle/working/submission.csv'
model = res_model(176)
model = model.to(device)
# 读取保存的最佳模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
model.eval()
predictions = []
for batch in tqdm(test_loader):
imgs = batch
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(imgs.to(device))
predictions.extend(logits.argmax(dim=-1).cpu().numpy().tolist())
preds = []
for i in predictions:
preds.append(num_to_class[i])
test_data = pd.read_csv(test_path)
test_data['label'] = pd.Series(preds)
submission = pd.concat([test_data['image'], test_data['label']], axis=1)
submission.to_csv(saveFileName, index=False)